General Information About Paranasal Sinus and Nasal Cavity Cancer
- Paranasal sinus and nasal cavity cancer arises from the tissues of the paranasal sinuses and nasal cavity.
- Different types of cells in the paranasal sinus and nasal cavity may become cancerous.
- Being exposed to certain chemicals or dust in the workplace can increase the risk of paranasal sinus and nasal cavity cancer.
- Signs of paranasal sinus and nasal cavity cancer include sinus problems and nosebleeds.
Paranasal sinus and nasal cavity cancer arises from the tissues of the paranasal sinuses and nasal cavity.
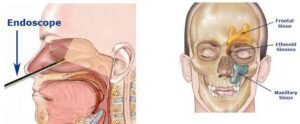
Paranasal sinuses
“Paranasal” means near the nose. The sinuses are hollow, air-filled spaces in the bones around the nose.
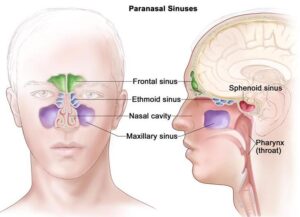
There are several paranasal sinuses:
- Frontal sinuses (forehead above the nose)
- Maxillary sinuses(within the upper jaw bone)
- Ethmoid sinuses(between the eyes).
- Sphenoid sinus (behind the nose, in the centre of theskull)
Nasal cavity
The nose opens into the nasal cavity, which is divided into two nasal passages.
Together the paranasal sinuses and the nasal cavity filter and warm the air, and make it moist before it goes into the lungs.
Different types of cells in the paranasal sinus and nasal cavity may become malignant.
The most common type of paranasal sinus and nasal cavity cancer is squamous cell carcinoma.
Other types of paranasal sinus and nasal cavity cancer include the following:
- Melanoma
- Sarcoma
- Inverting papilloma
Being exposed to certain chemicals or dust in the workplace can increase the risk of paranasal sinus and nasal cavity cancer.
Risk factors for paranasal sinus and nasal cavity cancer include the following:
- Being exposed to certain workplacechemicals or dust, such as those found in the following jobs:
- Furniture-making.
- Woodworking (carpentry).
- Metal-plating.
- Flour mill or bakery work.
- Beinginfected with human papillomavirus (HPV).
- Being male and older than 40 years.
Signs of paranasal sinus and nasal cavity cancer include sinus problems and nosebleeds.
Check with your doctor if you have any of the following:
- Blocked sinuses that do not clear, or sinus pressure.
- Headaches or pain in the sinus areas.
- A sore inside the nose that does not heal.
- A lump on the face or roof of the mouth.
- Numbness or tingling of the face.
- Double vision
- Pain in the upper teeth, loose teeth, or dentures that no longer fit well.
- Earache
Examination, diagnosis, investigations
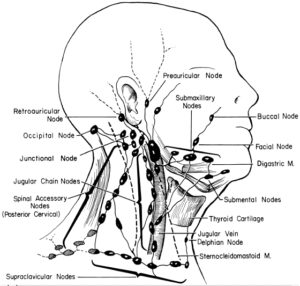
- Clinical examination and history: Your OMFS H&N surgeon will ask about your social habits (smoking and drinking) and take a thorough medical history. The neck will be felt for swollenlymph nodes.
- Biopsy:This is paramount in order to diagnose cancer. Your OMFS H&N Surgeon will take a sample of the abnormal area.
- Fiberoptic nasoendoscopy: Your OMFS H&N surgeon will pass a thin tube-like camera through your nose, to examine the back of your nose, your throat, the base of your tongue and your voice box (larynx).
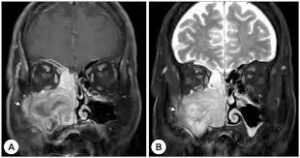
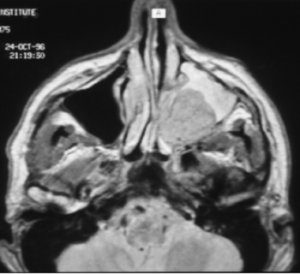
- MRI(Magnetic Resonance Imaging): A procedure that uses a magnet, radio waves, and a computer to make a series of detailed pictures of areas inside the body. An MRI of your H&N region is required to stage the cancer.
- CT scan F5: A computerised x-ray that makes a series of detailed pictures of areas inside the body, taken from different angles. A CT scan of your thorax (chest) is needed for staging H&N cancer, to exclude disease spread and/or second primaries in the lung.
Factors affecting the outcome
The prognosis (chance of cure and recovery) depends on:
- The fitness of the patient
- Whether the patient is/was a smoker.
- The stageof the cancer.
- The type of the cancer (how does it look under the microscope)
- The location of the cancer.
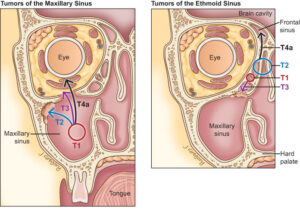
Stages of Paranasal Sinus and Nasal Cavity Cancer
KEY POINTS
- There are three ways that cancer spreads in the body.
- Cancer may spread from where it began to other parts of the body.
- The following stages are used for laryngeal cancer:
- Stage 0 (Carcinoma in Situ)
- Stage I
- Stage II
- Stage III
- Stage IV
The way paranasal sinus and nasal cavity cancer is staged is complex – your OMFS H&N surgeon will explain the stage and the implications once all tests are completed.
The process used to find out if cancer has spread to other parts of the body is called staging. Staging guides decision-making and treatment.
There are three main ways that cancer spreads in the body.
Cancer can spread through tissue, the lymph system, and the blood:
- The cancer spreads from where it began by growing into nearby areas. Some types of cancer prefer to spread across nerves (perineural spread)
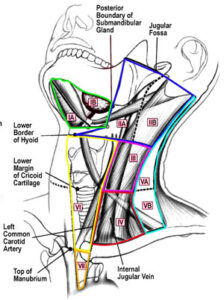
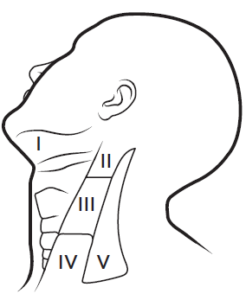
- Lymph system. The cancer spreads to the lymph glands (in H&N cancer it spreads in the neck lymph glands).
- The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the blood. The cancer travels through theblood vessels to other parts of the body (distant metastasis).
When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis.
Treatment
- When possible, the primary treatment for nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses cancer, is surgery
- Maxillary sinus tumours are treated the same way as any other mouth cancer (see chapter)
- Radiotherapy is used as adjuvant treatment after surgery in selected cases
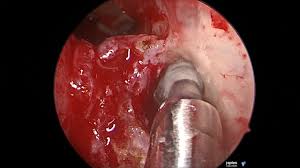
- Endoscopic surgical resection is an option for specific types of cancers that are inaccessible to open surgery.
- Two types of standard treatment are used:
- Surgery(primary treatment)
- Radiation therapy (adjuvant or primary for specific types/locations)
- Treatment for nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses cancer, is difficult, complex and may cause side effects.
- Follow-up tests may be needed.
Patients with nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses cancer, should have their treatment planned by a team of doctors who are expert in treating head and neck cancer.
Your expert OMFS/H&N Surgeon, who will guide the team for you, will oversee your treatment. A team approach is required to overcome the potential side effects of the treatment. The team usually include:
- Head and necksurgeon (ablation and reconstruction)
- Radiation oncologist
- Speech therapist
- Dietitian
- Pathologist
- Radiologist
- CNS
Surgery
Surgery (removing the cancer in an operation) can be used for nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses cancers. Surgery might include the following:
- Wide local excision of the tumour: The OMFS H&N Surgeon will remove the tumour with a margin of healthy surrounding tissue
- Endoscopic resection: The OMFS H&N Surgeon will remove the tumour through your nose, with the help of a camera (endoscope)
- Neck dissection: Removal oflymph nodes in the neck. This is done when cancer has or may have spread from the primary side. This also provides access to blood vessels for microvascular reconstruction.
- Reconstruction: In cases that the resection of the cancer includes surrounding structures (skin, bone, oral cavity mucosa) your OMFS Surgeon will discuss reconstruction options with you. This is a highly demanding and highly important part of your cancer treatment. The defect created by the removal of the tumour needs to be re-build to improve function and reduce the risk of potential side effects. The gold standard is the use of microvascular free tissue transfer (the surgeon takes tissue – skin, muscle, bone or combinations – from other parts of the patients’ body, preserving the blood vessels and re-perfuses the flap by anastomosing the blood vessels with donor vessels in the neck. This is called microvascular surgery and it is done under the operating microscope. Offering this kind of treatment should be the minimum you would expect from your OMFS H&N Surgeon.
Radiatiotherapy
Radiatiotherapy is a cancer treatment that uses high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells or keep them from growing.
Side Effects
Treatment for nasal cavity and paranasal sinus cancer is difficult and can result in life-changing side effects. Your OMFS H&N surgeon will follow you up and try to deal with these side effects whenever possible
- Xerostomia – dry mouth
- Difficulties in speech
- Difficulties in swallowing (may require feeding tube)
- Changes in appearance
- Weight loss
- Infection
- Lymphedema
- Chronic pain
- Osteoradionecrosis (ORN)
- Shoulder dysfunction
- Taste changes
- Scarring
- Visual disturbances