Pre-prosthetic surgery
This includes any surgery on the jawbone or the soft tissues of the mouth that is done in preparation for prosthetic dental rehabilitation.
The type of surgery is tailored on each individual patient’s needs. Some commonly used procedures include:
- Alveoloplasty: This is essentially trimming and refashioning of the alveolar bone (they bone that surrounds and supports the teeth) following dental extractions, so that the jaws can accept dentures or implants.
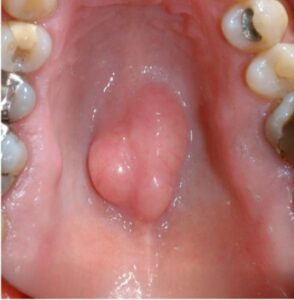
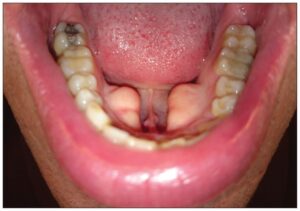
- Removal of tori or exostosis: Some patients have extra pieces of bone (exostoses) attached to their jawbone. This is common and completely benign. If they appear on the lingual surface of the mandible, they are known as tori mandibulari, whereas if they appear on the middle of the hard palate, they are called torus palatinus. These exostoses can interfere with the fitting of dentures and your OMFS surgeon will remove them and smooth the underlying bone with a bur.
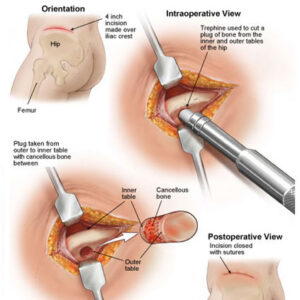
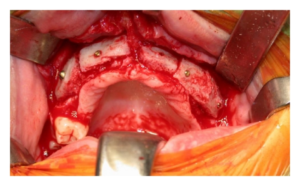
- Bone grafting: Occasionally, the remaining jawbone might not be enough to support dentures or implants. Therefore your OMFS surgeon might use bone grafts to enhance the size of the alveolar bone, so that you can have dental rehabilitation. There are several types of bone grafts. An autograft is taken for the patient’s own body. An allograft is harvested from deceased donors and undergoes preparation to be used safely in other humans. A xenograft comes from other species (usually porcine or bovine). Finally, an alloplastic graft is composed from material not taken from human or animal sources, and it can be natural or synthetic (i.e. hydroxyapatite). When it comes to bone grafting for the jaws, the most commonly used graft types are autografts in combination with xenografts.
- Autografts can be taken form inside the mouth (chin or ramus of the mandible) or from other areas of the body. When large bone stock is required, your OMFS surgeon will harvest bone from your hip, in the form of a bone block and bony particles. This procedure needs to be done under general anaesthetic and you may need to stay in the hospital overnight, as the hip wound might bleed. Bone grafts are secured in the recipient side of the jaw using a combination of titanium screws and membranes.
Removal of excess soft tissue
Sometimes, gums can become hyperplastic and won’t allow the placement of dentures or implants. Your OMFS surgeon will remove the excess soft tissue and re-suture the gums in the appropriate fashion.